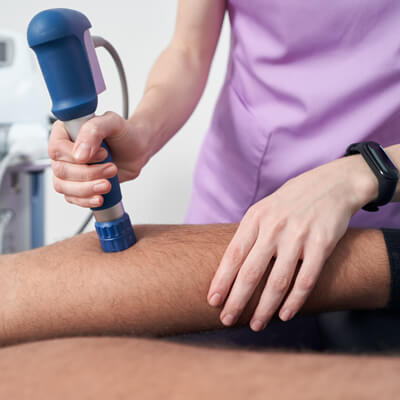
 Plantar fasciitis is a common and often debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide, especially those who are active or overweight. Characterized by pain in the heel and along the bottom of the foot, plantar fasciitis can significantly impair a person’s quality of life. One of the most effective treatments for this condition is Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT), a non-invasive method that has been gaining attention for its success in managing pain and promoting tissue healing.
Plantar fasciitis is a common and often debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide, especially those who are active or overweight. Characterized by pain in the heel and along the bottom of the foot, plantar fasciitis can significantly impair a person’s quality of life. One of the most effective treatments for this condition is Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT), a non-invasive method that has been gaining attention for its success in managing pain and promoting tissue healing.
In this blog, we will delve into the research behind shockwave therapy and its effectiveness in treating plantar fasciitis, drawing on a comprehensive review of available studies. By understanding the benefits of ESWT, patients can make informed decisions about their treatment options.
What Is Plantar Fasciitis?
Plantar fasciitis is a degenerative condition affecting the plantar fascia, a thick band of tissue that connects the heel to the toes and supports the arch of the foot. This condition is most commonly seen in individuals aged 40 to 60, but it also affects athletes, especially runners, as well as those with high body mass indexes (BMIs). Symptoms include sharp, stabbing pain in the heel, particularly after periods of inactivity or following weight-bearing activities.
Although historically considered an inflammatory condition, more recent research suggests that plantar fasciitis is better understood as a degenerative disorder, sometimes referred to as “fasciopathy” or “fasciosis.” The condition is persistent and can take months or even years to resolve without appropriate treatment.
The Role of Shockwave Therapy in Treating Plantar Fasciitis
Shockwave therapy works by delivering high-energy acoustic waves to the affected area, which stimulates the body’s natural healing process. The therapy encourages neovascularization (the formation of new blood vessels), improves blood flow, and helps reduce inflammation in the plantar fascia. This treatment has been extensively researched and is becoming a preferred option for patients seeking relief from plantar fasciitis.
Research Findings on the Effectiveness of ESWT
A 2021 comprehensive review analyzed systematic reviews and meta-analyses on plantar fasciitis treatment, including the effectiveness of ESWT. The review found consistent evidence supporting ESWT as an effective treatment for plantar fasciitis, particularly for patients who had not responded to other treatments like corticosteroid injections, physical therapy, or orthotics.
The key findings from the review include:

- Reduction in Pain: ESWT has been shown to significantly reduce pain in individuals with plantar fasciitis. Studies found that patients receiving shockwave therapy reported a marked decrease in pain levels compared to those receiving placebo treatments or other conservative therapies. This reduction in pain was often seen within weeks of treatment, with continued improvements over several months.
- Improved Functional Outcomes: Alongside pain reduction, ESWT has been shown to improve overall foot function, allowing patients to return to daily activities without discomfort. Many studies reviewed in the meta-analysis highlighted improvements in mobility, reduced pain during walking, and better tolerance for weight-bearing activities.
- Long-Term Benefits: One of the most promising aspects of ESWT is its ability to deliver long-term benefits. Unlike treatments such as corticosteroid injections, which may provide only temporary relief, shockwave therapy has been shown to have sustained effects, with improvements in both pain and function lasting for months or even years after the initial treatment.
- Low Risk of Complications: The review also pointed out that ESWT is a low-risk, non-invasive option compared to surgery or repeated injections. The treatment involves no incisions or anesthesia and has minimal side effects, which makes it an appealing choice for those looking to avoid more invasive procedures.
BMI and Risk Factors for Plantar Fasciitis
The systematic review also explored various risk factors for plantar fasciitis, with one of the most significant being a higher BMI. Studies have consistently shown that individuals with higher body weight are more prone to developing plantar fasciitis, particularly those who are not engaged in regular physical activity. For non-athletic populations, the strain on the plantar fascia caused by excessive weight can lead to the microtears and degeneration characteristic of plantar fasciitis.
In these cases, shockwave therapy has proven to be an effective treatment option, helping alleviate the chronic pain associated with plantar fasciitis, even when weight loss or other lifestyle changes are challenging to implement.
How Does ESWT Compare to Other Treatments?
The systematic review highlights that while ESWT is effective, it is not the only treatment option available for plantar fasciitis. Other common treatments include:
- Corticosteroid Injections: While injections can provide short-term relief, they often come with risks such as plantar fascia rupture and recurrence of symptoms after the effects of the injection wear off. Studies have shown that while corticosteroids can reduce pain in the short term (up to one month), they are less effective in the long term compared to ESWT.
- Physical Therapy and Stretching Exercises: Physical therapy, including stretching exercises and manual therapy, is often recommended as a first-line treatment for plantar fasciitis. However, for individuals who do not see improvement with these conservative methods, ESWT can be a valuable next step.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP involves injecting a patient’s own blood platelets into the injured area to promote healing. While PRP shows promise in some studies, its effectiveness compared to ESWT is still being researched. The systematic review notes that PRP may offer benefits similar to ESWT but with greater variability in outcomes.
Why Choose Shockwave Therapy?
For patients suffering from chronic plantar fasciitis, shockwave therapy offers several distinct advantages over other treatments:
- Non-Invasive: There is no need for surgery, injections, or invasive procedures. ESWT is a non-surgical solution that can be administered in a clinic setting.
- Fast Recovery Time: Patients can often return to normal activities quickly after treatment, making it a convenient option for those with busy schedules.
- Proven Effectiveness: Numerous studies have shown that ESWT is effective in reducing pain and improving function in patients with plantar fasciitis.
- Minimal Side Effects: Unlike corticosteroid injections or surgery, ESWT has minimal side effects and risks. Common side effects, such as mild discomfort or redness, usually resolve within a few days.
Conclusion
For individuals who are struggling with the persistent pain of plantar fasciitis, Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy (ESWT) offers a highly effective, non-invasive treatment option. Research shows that shockwave therapy can significantly reduce pain, improve mobility, and provide long-term relief, all while avoiding the risks associated with more invasive procedures.
At HealthyWays Integrated Wellness Solutions, we offer cutting-edge shockwave therapy to help you get back on your feet, pain-free. If you’re tired of living with plantar fasciitis and haven’t found relief through other treatments, shockwave therapy could be the solution you’ve been looking for. Contact us today to learn more about how shockwave therapy can help you reclaim your mobility and live pain-free.
